Ivan Gerdzhikov, Department of Prosthetic dentistry, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Medical University – Sofia, Bulgaria.
ABSTRACT:
Introduction: The prosthetic treatment in patient with alveolar resorption is very difficult, and sometimes it is possible only after surgical preparation of the pros- thetic field. In the cases, where surgical lift of the soft tis- sues in the vestibulum is performed, a forming denture, which has to shape the denture-bearing area, is required to design the healing of the soft tissues.
Aim: The aim of the described method is to present the abilities of the forming dentures with silicone base, for conducting surgical preparation of prosthetic treat- ment in patients with resorption of the alveolar bone.
Materials and methods: The prosthetic rehabilita- tion of 54-years-old female patient with complete edentulism and maxillary resorption, as a result of unsuc- cessful implant treatment with subperiosteal net, is de- scribed. After its surgical removal a complete dentures of the both jaws were made. The upper denture was used as a custom tray for taking impression with additive silicone, during the vestibuloplasty. The impression material was substituted with one-component heat-cured silicone Molloplast B in the dental laboratory and the denture was finished on the classical technology. After cleaning, pol- ishing and disinfection , the denture was adjusted and ar- ticulated in patient’s mouth.
Results: The described methodology of prosthetic treatment and fabrication of forming denture allowed suc- cessful surgical treatment. The silicone base reduced the masticatory pressure and provided atraumatic conditions for the healing process. The vestibuloplasty ensured den- ture’s retention and stability, which helped patient’s chew- ing, feeding and speaking.
Conclusion: The application of appropriate meth- odology and technique for fabrication of forming dentures provides successful design of the vestibulum and denture- bearing area. This facilitates the conducting of the fol- lowing prosthetic treatment.
Key words: forming denture, denture-bearing area, complete denture, silicone relining material.
INTRODUCTION
Forming dentures are common applied devices in treatment of patients with maxillofacial disorders. They provide appropriate hard base for conducting of plastic surgery and shaping of soft tissue box. They also determine the growth and healing path of the soft tissue (1, 2). Different materials and methods are used for their fabri- cation, which increases the treatment effect and improves patients’ life quality (3, 4).
The acrylic dentures with silicone base are commonly used in treatment of edentulous patients. The rea- son for this is that these dentures provide good masticatory function, retention and oral hygiene (5). The researches revealed, that the denture’s silicone is non toxic, tissue compatible material, which does not cause trauma or irritation (6,7). Its application is very appropriate in patients with alveolar resorption, retentive tubers or irregular bone atrophy (8). The electromiographic examinations shows, that treatment with silicone based dentures increases the activity of temporal and masseter muscles and chewing efficiency (9, 10).
The main problem in fabrication of silicone based dentures is creating of a reliable and durable connection with the acrylic resin (11). This imposes a preliminary preparation of denture’s surface with different materials and methods. Some authors (12, 13) use phosphoric acid, as an etching device for the borders of the denture, but others create micro retentions with lasers (14). The investigations discovered, that preliminary rib of the acrylic resin with monomer increases the connection with the silicone material, and sandblasting procedures reduces it (15). Better long lasting adhesion is achieved when heat cured silicone materials are used and the polymerization of both materials is performed in the same time (16, 17).
There is a lot of data in the literature, about the quality and properties of the materials, used for relining of dentures (5, 6, 8). According to some of them, Molloplast B is the optimum silicone material for this purpose (11). The researches show its good adhesion with the acrylic resin, which provides long lasting connection and stability (18). Polysiloxane base of the material pro- vides the preserving of soft and smooth surface, which prevents from accumulation of plaque and facilitates den- ture’s cleaning (19, 20). These advantages are very important, because of other investigations, which reveals, that the porous surface of the silicone materials create a precondition for Candida albicans growth (21). Disinfectants are recommended for solving this problem, but they coloring the dentures and destroy the connection with the acrylic resin (22). The examinations say, that the application of appropriate silicone materials and methods for cleaning prevent the coloring and prolong the expiration date of the denture (23, 24).
AIM
The aim of the described method is to present the abilities of the forming dentures with silicone base, for conducting surgical preparation of prosthetic treatment in patients with resorption of the alveolar bone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The clinical case described the prosthetic treatment of 54-years-old woman with complete edentulism and maxillary resorption, due to unsuccessful implant treat- ment with subperiosteal net and fixed constructions (fig. 1). Surgical treatment for net elimination was performed, because of infection. After this, the patient is advised to make consultation with prosthetic treatment specialist. The intraoral examination revealed severe maxillary bone resorption, without any teeth left. The healing process af- ter the surgery had not been completed and the treatment was deferred (fig. 2).
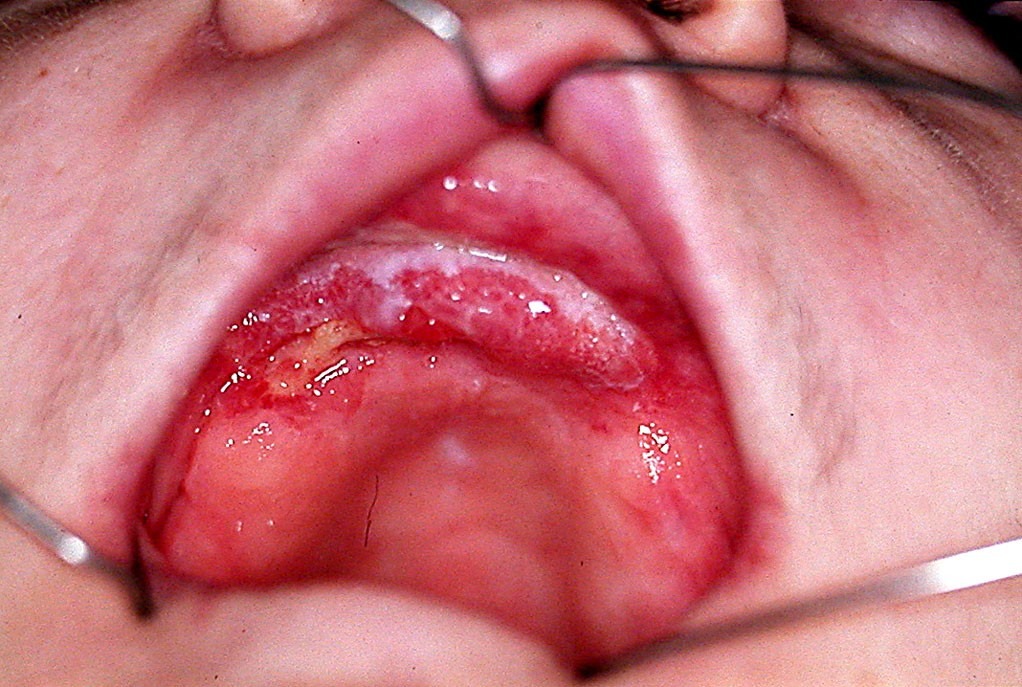
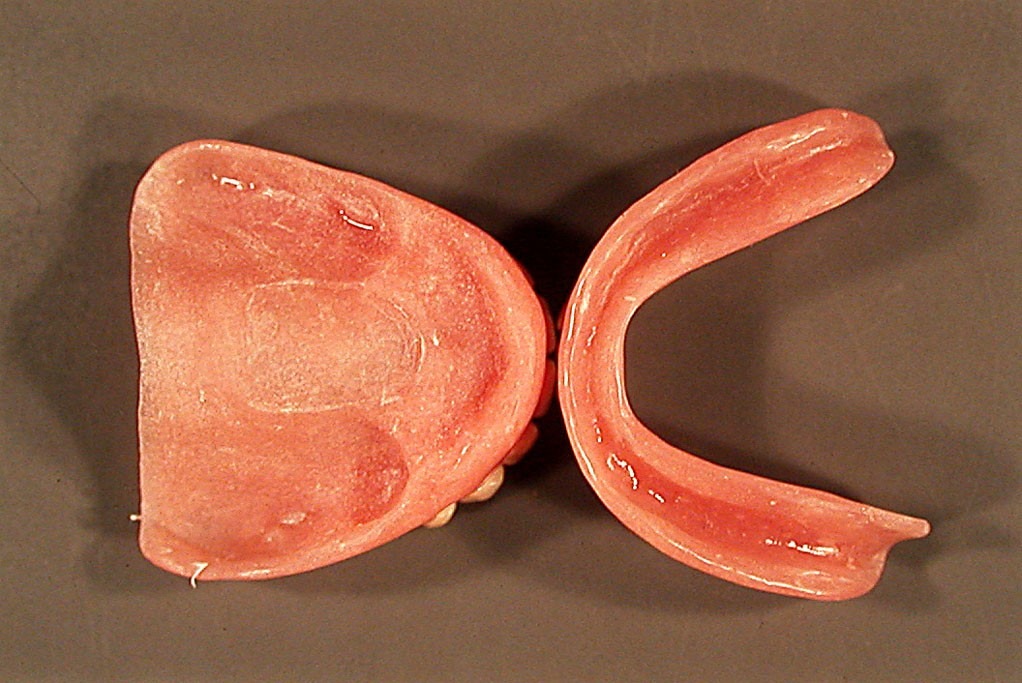
The examination after one month showed significant bone resorption with unfavorable prognosis (fig. 3). A treatment plant was compiled, which involved prelimi- nary surgical preparation in the vestibulum of the maxilla. The fabrication of forming denture with silicone base in the upper jaw and complete denture in the lower jaw was planned. The preliminary impressions were taken with standard trays and irreversible hydrocolloid impres- sion material and the finals were taken with custom trays and additive silicone. The dentures were fabricated, according to the classical technique. During the operation, after the flap preparation and vestibuloplasty, a new im- pression was taken with additive silicone and the denture, as an individual tray. It was followed by immediate flasking in the laboratory. The impression material was substituted with one-component heatcured silicone Molloplast B (DETAX GmbH & Co. KG). An air chamber was formed for additional retention and stability (fig. 4). The dentures, polished and disinfected, were adjusted and articulated in patient’s mouth immediately after the surgery. Regular examinations, for decubitus wounds and occlusal disturbances, were performed while the healing process completed.
RESULTS
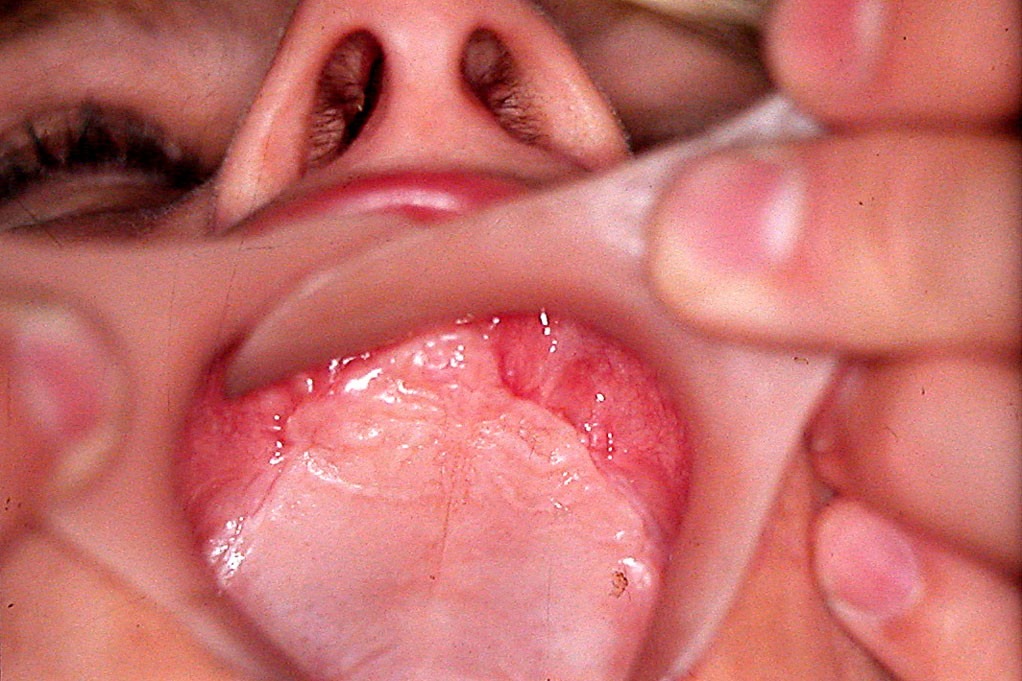
The results of the conducted treatment revealed successful soft tissue design in the denture bearing area, which provided the needed retention and stability (fig. 5). The normal occlusal relationships were restored, which allowed normalization of patient’s chewing and feeding (fig. 6). The healing processes went without any compli- cations or soft tissue decubitus wounds. During the check- ups were made only small occlusion corrections. After the end of the healing process was formed a vestibulum with clearly expressed denture bearing area and maxillary tu- bers, which was the main goal of the treatment (fig. 7). The prepared denture base up provided conditions for flawless future prosthetic treatment with complete dentures.
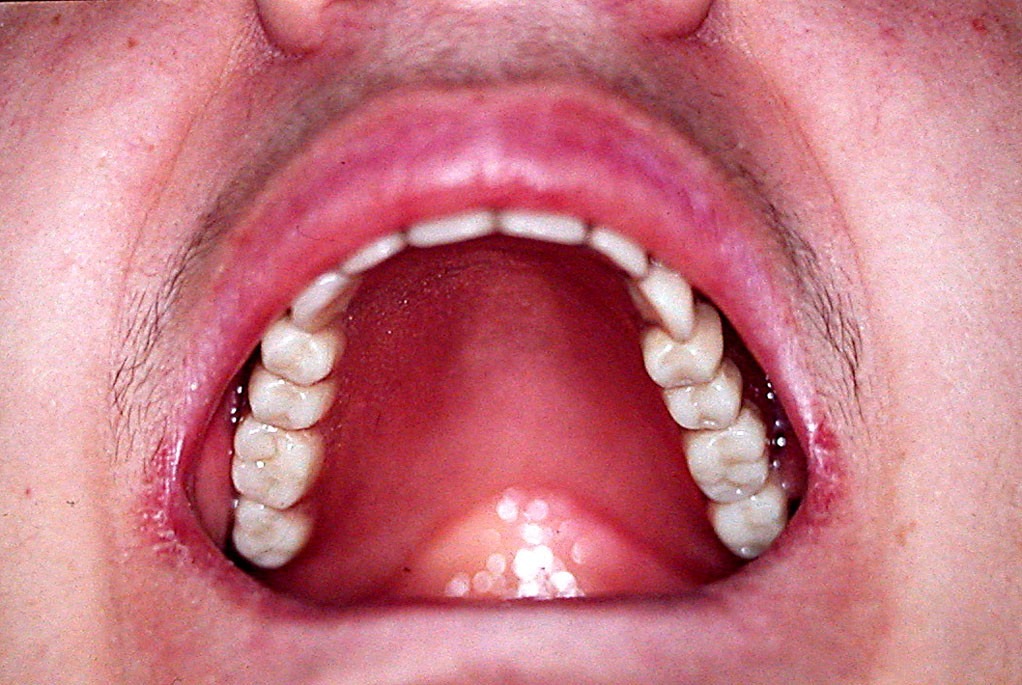
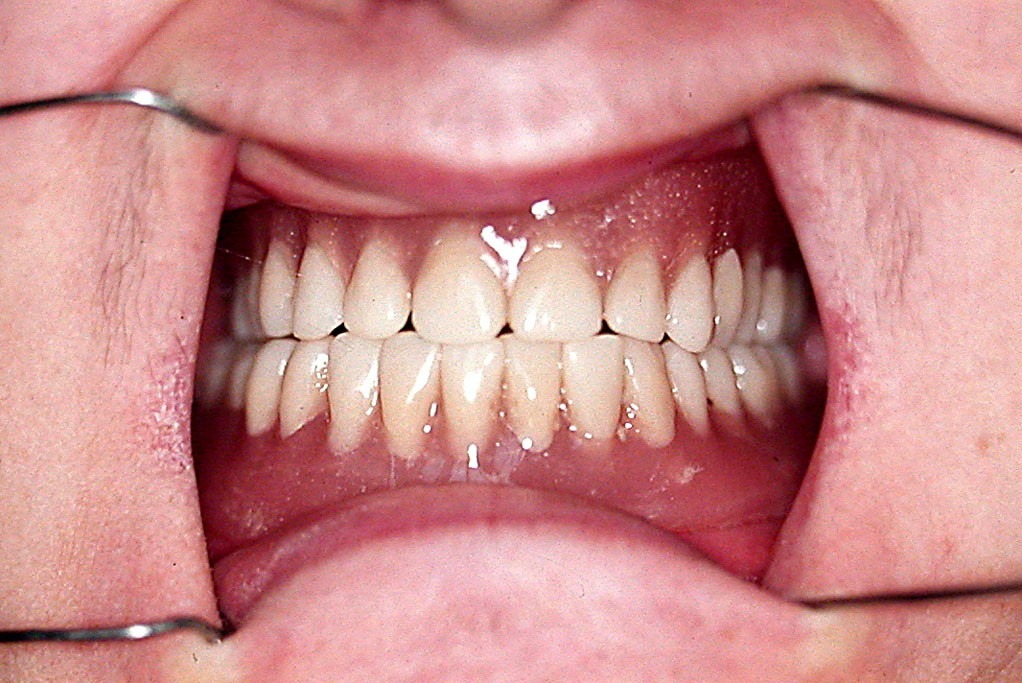
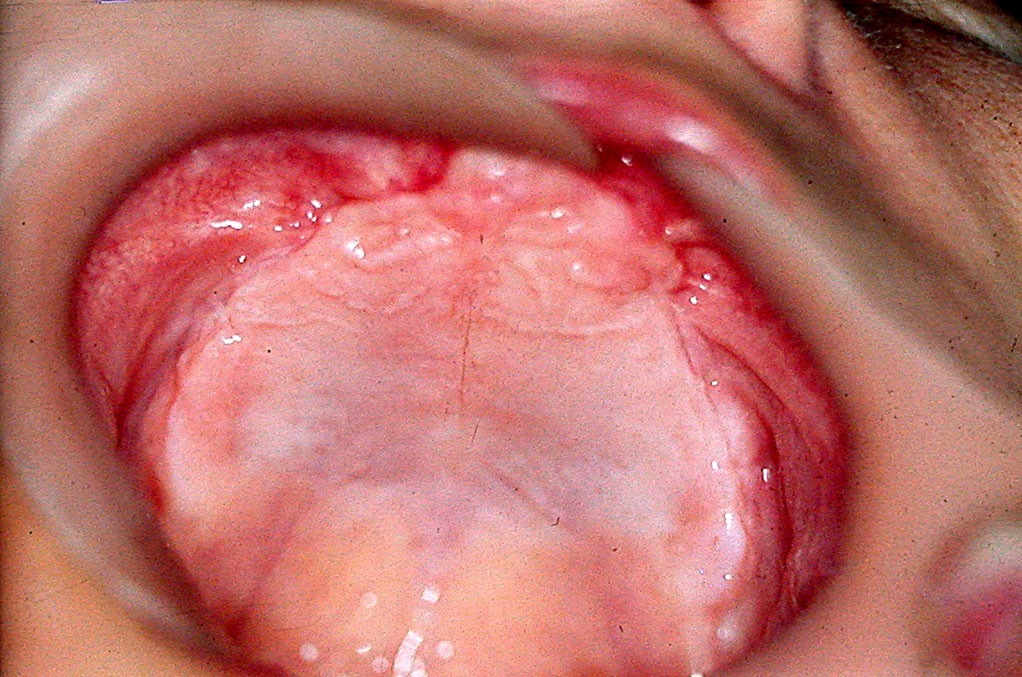
DISCUSSION
The prosthetic treatment in patient with complete edentulism is accompanied by many difficulties and prob- lems, which are connected with insurance of good reten- tion and stability. Often, the alveolar bone resorption dis- rupts dentures’ retention, which leads to the application of surgical treatment methods and preparation of the den- ture’s base up. This sometimes includes a flap technique in the area of the vestibulum and design of an appropriate dental bearing area. Forming dentures, which deter- mine the shape of the healing soft tissue and formed a soft tissue box, are required for successful surgical treatment. The applied materials and methods should provide a nor- mal healing process and atraumatic masticatory pressure delivery. The numerous advantages of the silicone materials were used in this clinical case. The achieved results confirmed the state, that their application provide opti- mum retention and stability (5, 8). This allowed successful restoration of the masticatory function and showed, that silicone materials improved the chewing efficiency, which other authors report (9, 10). The normal healing process and the luck of decutibus wounds proved, that the denture silicone is non toxic, biocompatible material, as most of the authors claim (6, 7). The data from some researches, for uncertainty and temporary connection with the acrylic resin, was not confirmed (11). The heatcured silicone Molloplast B was chosen, which is considered as the best option for this type of treatment. The clinical results revealed good adhesion with the acrylic resin, which confirmed the state of many authors (18). During the follow-up appointments we did not establish any hardening or waste of silicone elasticity. The polysiloxane surface remained soft and smooth, which facilitated denture’s cleaning. The application of antibacterial soap and soft brush did not affect the connection with the acrylic resin or colored the denture, as well, which some researches claim to happen (22). This improved the state, that the choice of appropriate silicone materials, methods and cleaning tools prevent denture’s coloring and prolong the expire date (23, 24).
CONCLUSION
The application of the specific methodology and materials for fabrication of forming dentures allows successful design of the vestibulum and dental bearing area, which allows the conduction of the prosthetic treatment. Even though it is related with surgical intervention, the forming prosthetic treatment is an alternative of patients, who refuse or have contraindications for implant treatment.
REFERENCES:
- Huryn JM, Piro JD. The maxil- lary imediate surgical obturator pros- thesis. J Prosthet Dent. 1989 Mar;61(3):343-7. [PubMed]
- Frame RT, King GE. A surgical interim prosthesis. J Prosthet Dent. 1981 Jan;45(1):108-10. [PubMed]
- Garg AK, Malo M, Dorado L, Duarte F. Postsurgical management with maxillary obturators after maxillectomy. Gen Dent. 1998 Jan- Feb;46(1):75-78. [PubMed]
- El Fattah H, Zaghloul A, Pedemonte E, Escuin T. Pre-prosthetic surgical alterations in maxillectomy to enhance the prosthetic prognoses as part of rehabilitation of oral can- cer patient. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2012 Mar 1;17(2):262-70. [PubMed]
- Kruniæ N, Kostiæ M, Petroviæ M, Igiæ M. Oral health-related qual- ity of life of edentulous patients af- ter complete dentures relining. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2015 Apr;72(4):307- 6 [PubMed]
- Atay A, Bozok Cetintas V, Cal E, Kosova B, Kesercioglu A, Guneri P. Cytotoxicity of hard and soft den- ture lining materials. Dent Mater J. 2012; 31(6):1082-6 [PubMed]
- Sukumaran P, Fenlon MR. Two- piece obturator using “lock-and-key” mechanism. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2017 Apr-Jun;17(2):207-211. [PubMed]
- Mendez M, Lee C. Use of a per- manent soft denture liner in the retromylohyoid eminence and knife- edge ridge areas of the mandible to aid in retention and stability. Gen Dent. 2013 Nov-Dec;61(7):14-5. [PubMed]
- Rastogi A, Srivastava S, Gaur A, Dupare A, Rastogi S, Kamatagi L. Electromyographic Evaluation of the Effect of Lined Dentures on Mastica- tory Muscle Activity in Edentulous Subjects. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Aug;9(8):80-3. [PubMed]
- Pisani MX, Segundo AL, Leite VM, de Souza RF, da Silva MA, da Silva CH. Electromyography of mas- ticatory muscles after denture relining with soft and hard denture liners. J Oral Sci. 2013 Sep;55(3):217-24. [PubMed]
- Tugut F, Coskun ME, Dogan DO, Kirmali O, Akin H. Tensile Bond Strength between Soft Liners and Two Chemically Different Denture Base Materials: Effect of Thermocycling. J Prosthodont. 2016 Jun;25(4):319-23. [PubMed]
- Kaur H, Datta K. Comparative evaluation of tensile bond strength of silicone-based denture liners after thermocycling and surface treatment. Indian J Dent Res. 2015 Sep- Oct;26(5):514-9. [PubMed]
- Gundogdu M, Yesil Duymus Z, Alkurt M. Effect of surface treatments on the bond strength of soft denture lining materials to an acrylic resin denture base. J Prosthet Dent. 2014 Oct;112(4):964-71. [PubMed]
- Gorler O, Dogan DO, Ulgey M, Goze A, Hubbezoglu I, Zan R, et al. The Effects of Er:YAG, Nd:YAG, and Ho:YAG Laser Surface Treatments to Acrylic Resin Denture Bases on the Tensile Bond Strength of Silicone- Based Resilient Liners. Photomed La- ser Surg. 2015 Aug;33(8):409-14. [PubMed]
- Kulkarni RS, Parkhedkar R. The effect of denture base surface pretreatments on bond strengths of two long term resilient liners. J Adv Prosthodont. 2011 Mar;3(1):16-9. [PubMed]
- Madan N, Datta K. Evaluation of tensile bond strength of heat cure and autopolymerizing silicone-based resilient denture liners before and af- ter thermocycling. Indian J Dent Res. 2012 Jan-Feb;23(1):64-8. [PubMed]
- Demir H, Dogan A, Dogan OM, Keskin S, Bolayir G, Soygun K. Peel bond strength of two silicone soft lin- ers to a heat-cured denture base resin. J Adhes Dent. 2011 Dec;13(6):579- 84 [PubMed]
- Salloum AM. Effect of Aging on Bond Strength of Two Soft Lining Materials to a Denture Base Polymer. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014 Dec;14(1):155-60. [PubMed]
- Mutluay MM, Tezvergil- Mutluay A. The influence of cyclic stress on surface properties of soft lin- ers. Odontology. 2017 Apr;105(2): 214-221. [PubMed]
- Araújo CU, Basting RT. In situ evaluation of surface roughness and micromorphology of temporary soft denture liner materials at different time intervals. Gerodontology. 2018 Mar;35(1):38-44. [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy S, Hallikeri- math RB. An In-vitro Evaluation of Retention, Colonization and Penetra- tion of Commonly Used Denture Lin- ing Materials By Candida albicans. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 Oct;10(10):84- 88[PubMed]
- Ekren O, Ozkomur A. Influ- ence of ozone and paracetic acid dis- infection on adhesion of resilient lin- ers to acrylic resin. J Adv Prostho- dont. 2016 Aug;8(4):290-5. [PubMed]
- Rao AK, Kumar S, Reddy NA, Reddy NS. The effect of denture cleansers on resiliency of soft lining materials. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013 Jan 1;14(1):65-70. [PubMed]
- Nowakowska-Toporowska A, Raszewski Z, Wieckiewicz W. Color change of soft silicone relining ma- terials after storage in artificial saliva. J Prosthet Dent. 2016 Mar; 115(3):377-80. [PubMed]
Please cite this article as: Gerdzhikov I. Methodology for fabrication of forming denture with silicone base. J of IMAB. 2018 Apr-Jun;24(2):2038-2042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018242.2038
Address for correspondence:
Dr. Ivan Gerdzhikov, Department of Prosthetic Dental Medicine, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Medical University – Sofia, 1, St. Georgi Sofiyski blvd., 1431Sofia, Bulgaria. e-mail: ivan_ger1971@abv.bg
